Planning for a secure and comfortable retirement requires a strategic approach to investing. This article will guide you through the essential steps to building significant wealth for your future, covering topics such as retirement planning, investment strategies, portfolio diversification, and risk management. Learn how to effectively save, invest, and grow your assets to achieve your retirement goals and enjoy a financially independent future.
Why Early Retirement Planning is Crucial

Early retirement planning offers a significant advantage: the power of compound interest. Starting early allows your investments to grow exponentially over a longer period, accumulating substantially more wealth than if you begin later.
Flexibility and choices are enhanced by early planning. You gain more control over your retirement timeline, allowing for potential early retirement or the option to pursue other life goals with greater financial freedom.
Early planning also helps mitigate the impact of unexpected events. Life throws curveballs; a robust retirement plan built early can provide a financial buffer against job loss, medical emergencies, or market fluctuations.
Reduced financial stress is another crucial benefit. Knowing you are financially prepared for retirement significantly reduces anxiety and allows you to enjoy your working years with greater peace of mind.
Finally, early planning provides the opportunity to strategically manage your investments, adjusting your portfolio to align with your risk tolerance and retirement goals over a longer timeframe.
How to Choose the Best Retirement Investment Accounts
Choosing the right retirement investment account is crucial for securing your financial future. Several factors influence this decision, primarily your income, tax bracket, and retirement goals.
401(k)s are employer-sponsored plans often offering matching contributions, making them attractive for maximizing savings. However, investment options are usually limited. Traditional IRAs offer tax-deductible contributions, reducing your current taxable income. Roth IRAs, conversely, offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement, but contributions aren’t tax-deductible. The best choice depends on your anticipated tax bracket in retirement.
SEP IRAs are simpler plans ideal for self-employed individuals or small business owners, offering high contribution limits. SIMPLE IRAs are another option for small businesses, providing a balance between contribution limits and administrative simplicity. Solo 401(k)s combine the advantages of a 401(k) and IRA, offering flexibility and higher contribution limits for self-employed individuals.
Consider consulting a financial advisor to determine which account best aligns with your specific circumstances. They can help you navigate the complexities of retirement planning and optimize your investment strategy based on your risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial objectives. Carefully evaluating your individual needs and available options is key to maximizing your retirement savings.
The Role of Stocks, Bonds, and Real Estate in Retirement Planning
Stocks, bonds, and real estate play crucial roles in a diversified retirement portfolio, each offering unique characteristics and risk profiles. A well-balanced approach leverages the strengths of each asset class to maximize returns while mitigating risk.
Stocks, representing ownership in companies, offer the potential for high growth over the long term, but also carry higher volatility. Their returns are tied to the performance of the underlying businesses and the overall economy. Therefore, they are generally considered suitable for long-term investors with higher risk tolerance.
Bonds, representing loans to governments or corporations, offer relatively lower returns compared to stocks but also significantly less risk. They provide stability and income through interest payments, serving as a ballast to offset stock market fluctuations. Bonds are typically suitable for investors seeking more conservative investment strategies.
Real estate provides diversification through tangible assets and potential rental income. It can offer inflation hedging and appreciation over time. However, real estate investments often require more management and liquidity can be limited compared to stocks and bonds. Its suitability depends on individual circumstances and investment goals.
The optimal allocation of assets among stocks, bonds, and real estate depends on factors such as individual risk tolerance, time horizon until retirement, and financial goals. Diversification across these asset classes is key to mitigating risk and building a robust retirement plan.
How to Calculate Your Retirement Needs
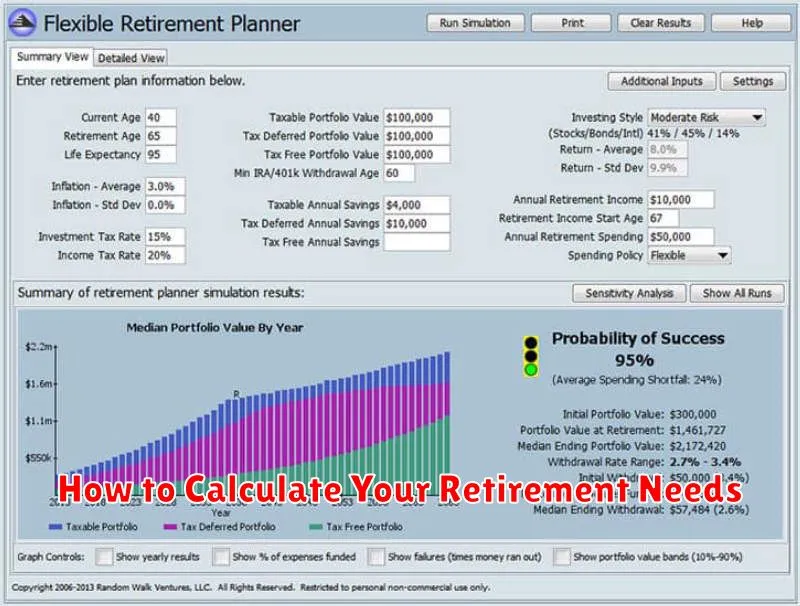
Accurately calculating your retirement needs involves several key steps. First, estimate your desired annual income in retirement. Consider your current lifestyle and desired level of spending. A common approach is to aim for 80% of your pre-retirement income, though this can vary based on individual circumstances.
Next, determine your retirement timeframe. This is the number of years you anticipate being in retirement. Longer timeframes necessitate larger savings.
Then, account for inflation. The cost of living will likely increase over time. Use an inflation rate to adjust your desired annual income for future years.
Calculate your total retirement savings needed by multiplying your adjusted annual income by your retirement timeframe. This provides a rough estimate of the total nest egg you will need.
Finally, factor in other income sources, such as Social Security or pensions, to potentially reduce the amount you need to save personally. Subtract these anticipated amounts from your total retirement savings need to determine your personal savings goal.
Remember, this is an estimate. Regularly review and adjust your calculations as your circumstances and financial goals change. Consider consulting a financial advisor for personalized guidance.
Best Low-Risk Investment Options for Retirement
Building a secure retirement requires a thoughtful investment strategy. For those prioritizing capital preservation over high growth, several low-risk options exist. High-yield savings accounts offer FDIC insurance and easy access to funds, although returns may lag inflation. Certificates of Deposit (CDs) provide fixed interest rates over a specified term, offering predictable returns but limiting liquidity. Treasury bonds, backed by the U.S. government, are considered among the safest investments, though returns can be modest.
Money market accounts (MMAs) combine features of savings accounts and money market funds, offering slightly higher interest rates than savings accounts with relatively easy access to funds. Government bonds issued by state and local governments offer slightly higher returns than treasury bonds, with a moderate level of risk. Annuities, while offering guaranteed income streams, may involve fees and limited access to funds, so careful consideration is needed before investing.
Diversification is key even within a low-risk portfolio. A balanced approach, potentially combining several of these options, can help mitigate risk while generating a steady income stream for retirement. It’s crucial to consult with a financial advisor to determine the optimal mix based on your individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and retirement goals. Professional financial guidance is essential for making informed decisions and building a secure retirement.
How to Generate Passive Income for Retirement
Generating passive income for retirement is crucial for financial security. This involves creating income streams that require minimal ongoing effort. Several avenues can help achieve this.
Real estate investment offers significant potential. Rental properties, REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts), or crowdfunding platforms provide options for passive income generation, though each carries varying levels of risk and management involvement.
Dividend-paying stocks are another popular choice. Investing in established companies that consistently pay dividends provides a steady stream of income. However, diversification is key to mitigate risk.
Peer-to-peer lending allows you to lend money to individuals or businesses, earning interest on your investment. This offers potentially higher returns but also carries higher risk compared to other passive income strategies.
High-yield savings accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs) provide a safer, albeit lower-return, form of passive income. They offer liquidity and stability, ideal for a portion of your retirement portfolio.
Building a successful passive income strategy requires careful planning, diversification, and risk assessment. Consider consulting a financial advisor to determine the most suitable approach based on your individual financial situation and risk tolerance.
The Impact of Inflation on Retirement Savings
Inflation significantly erodes the purchasing power of your retirement savings. Inflation is the gradual increase in the prices of goods and services over time. This means that the same amount of money will buy you less in the future than it does today.
For example, if your retirement savings grow at 5% annually, but inflation is at 3%, your real rate of return is only 2%. This reduced return means your savings won’t stretch as far in retirement as initially planned. High inflation can severely impact your retirement plans, potentially leaving you with insufficient funds to maintain your desired lifestyle.
To mitigate the impact of inflation, it’s crucial to invest in assets that historically outpace inflation. Stocks and real estate are often considered inflation hedges. Diversification across different asset classes can also reduce your portfolio’s vulnerability to inflationary pressures. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your investment strategy is essential to account for changing economic conditions and inflation rates. Consider working with a financial advisor to create a personalized plan that accounts for your unique circumstances and risk tolerance.
How to Adjust Your Investment Strategy as You Near Retirement

As retirement approaches, shifting your investment strategy becomes crucial to preserve capital and ensure a steady income stream. The primary goal transitions from aggressive growth to capital preservation and income generation.
Reduce risk by gradually decreasing your allocation to equities (stocks) and increasing your allocation to fixed-income investments (bonds). This minimizes potential losses from market volatility during your retirement years. A common approach is to use a glide path, systematically reducing equity exposure over time.
Consider diversifying into lower-risk investments such as government bonds, high-quality corporate bonds, and certificates of deposit (CDs). These offer relatively stable returns with lower volatility compared to stocks.
Assess your retirement income needs and adjust your investment strategy accordingly. Ensure you have sufficient funds to cover your anticipated expenses during retirement. This might involve exploring annuities or other income-generating investments.
Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio. Market conditions change, and your financial goals may evolve, necessitating adjustments to maintain a suitable risk profile and asset allocation. Seek professional financial advice to tailor your strategy to your specific circumstances.

