Are you looking to boost your investment portfolio’s returns and reduce risk? Options trading offers sophisticated investors a powerful tool to achieve these goals. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to effectively utilize options strategies, understand the intricacies of calls and puts, and ultimately, harness the power of options to enhance your overall investment performance. Learn how to strategically manage risk, capitalize on market volatility, and generate income through various options trading techniques.
What is Options Trading and How Does It Work?
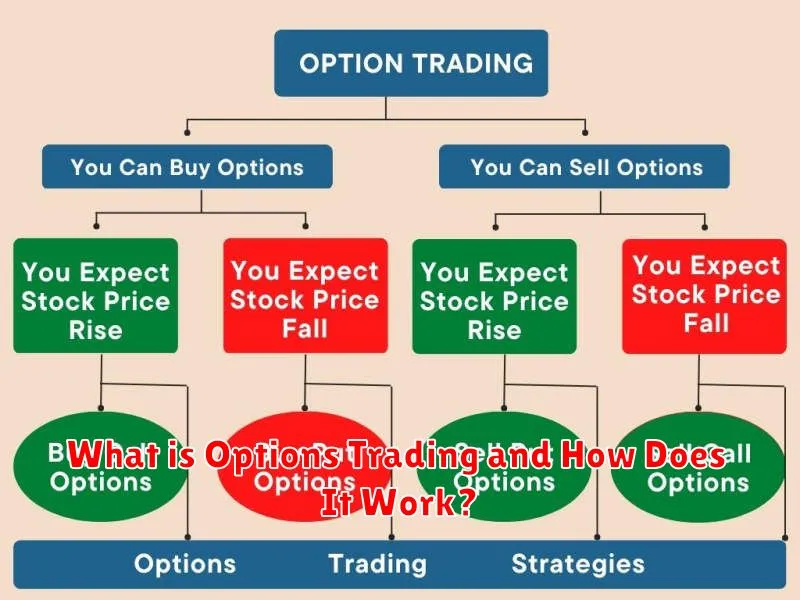
Options trading involves buying or selling options contracts, which grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset (like a stock) at a specific price (strike price) before or on a certain date (expiration date).
Call options are profitable if the underlying asset’s price rises above the strike price before expiration. Put options are profitable if the price falls below the strike price.
The buyer of an option pays a premium to the seller (the writer). The seller receives the premium but takes on the risk of potential losses if the option is exercised.
Options trading offers leverage, allowing investors to control a larger position with a smaller capital outlay compared to directly buying or selling the underlying asset. However, this leverage also magnifies both potential profits and losses.
Different strategies exist within options trading, each carrying its own risk profile and potential reward. Understanding these strategies is crucial before participating in options trading.
Understanding Call and Put Options
Options trading offers a powerful way to manage risk and potentially enhance returns in your investment portfolio. Call and put options are two fundamental contract types. Understanding their mechanics is crucial before engaging in options trading.
A call option grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase an underlying asset (like a stock) at a predetermined price (the strike price) before or on a specific date (the expiration date). The seller of the call option is obligated to sell the asset if the buyer exercises their right. Call options are typically bought when an investor anticipates the price of the underlying asset will rise.
Conversely, a put option grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price before or on the expiration date. The seller of the put option is obligated to buy the asset if the buyer exercises their right. Put options are generally bought when an investor believes the price of the underlying asset will fall.
Both call and put options have a premium, which is the price paid by the buyer to acquire the option. This premium is affected by several factors including the underlying asset’s price, volatility, time to expiration, and interest rates. Profit potential is theoretically unlimited for call options (if the underlying price rises significantly) and limited to the strike price minus the premium for put options. Conversely, maximum loss for buyers is limited to the premium paid, but sellers face potentially unlimited losses.
It’s vital to thoroughly understand the risks involved before trading options. Options contracts are complex instruments, and losses can occur quickly. Consider consulting a financial advisor before implementing options strategies in your portfolio.
The Role of Options in Hedging and Risk Management
Options contracts play a crucial role in hedging and risk management within an investment portfolio. They offer a flexible way to manage risk associated with existing asset holdings or anticipated future investments.
Hedging involves using options to mitigate potential losses. For example, a stock owner might purchase put options to protect against a decline in the stock’s price. If the price falls below the strike price of the put option, the investor can sell the stock at the higher strike price, limiting losses.
Options can also be used for speculative purposes, but this carries higher risk. While offering the potential for substantial gains, it also exposes investors to potentially significant losses if the underlying asset moves against the investor’s prediction.
The use of options in risk management strategies requires a strong understanding of option pricing models, market dynamics, and risk tolerance. It is essential to carefully assess the potential payoffs and risks associated with each strategy before implementation. Consult with a qualified financial advisor to determine suitability for your individual circumstances.
How to Generate Passive Income with Covered Calls
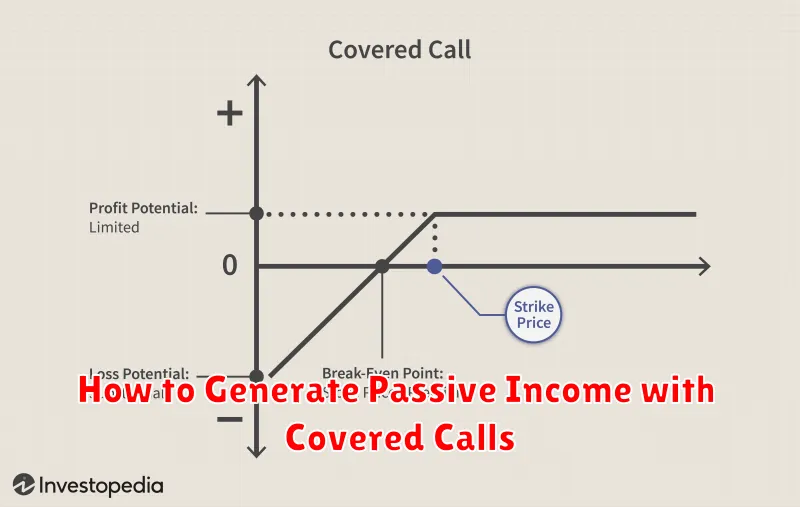
Covered calls are a popular options strategy used to generate passive income while owning a stock. It involves selling call options on shares you already own.
The process is straightforward: If you own 100 shares of a stock, you can sell one call option contract representing 100 shares. The buyer pays you a premium for the right, but not the obligation, to buy your shares at a specific price (the strike price) by a certain date (the expiration date).
Potential benefits include receiving the premium as immediate income, and potentially profiting even if the stock price remains flat or rises slightly below the strike price. However, your upside potential is capped at the strike price, and you risk having your shares called away if the price surpasses the strike price.
Risks include limited upside potential and the possibility of your shares being assigned (bought by the option buyer) before you are ready to sell. Thorough understanding of options trading is crucial before employing this strategy.
Careful stock selection is key. Choose stocks you are comfortable holding, even if the price rises above the strike price. Consider the stock’s volatility, the time to expiration, and the implied volatility when selecting strike price and expiration date.
Covered calls offer a way to potentially earn extra income from your existing stock portfolio, but are not without risk. It’s crucial to understand the intricacies of options trading before implementing this strategy.
Best Strategies for Beginners in Options Trading
For beginners, covered call writing offers a relatively low-risk approach. It involves selling call options on stocks you already own, generating income from premiums while limiting potential downside. This strategy benefits from owning the underlying asset, mitigating risk associated with option expiration.
Another accessible strategy is cash-secured puts. This involves selling put options, obligating you to buy the underlying stock at a specified price if the option is exercised. This strategy can be profitable if the stock price remains above the strike price, allowing you to keep the premium. However, it requires sufficient capital to purchase the shares if assigned.
Bull call spreads offer a defined-risk strategy for bullish investors. This involves buying a call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously selling a call option with a higher strike price on the same underlying asset and expiration date. The maximum profit is capped, and the maximum loss is defined, making it suitable for managing risk.
Bear put spreads are the bearish counterpart to bull call spreads. They involve buying a put option with a higher strike price and selling a put option with a lower strike price. This strategy profits when the underlying asset price declines, offering defined risk and profit potential.
Important Note: Options trading involves significant risk and is not suitable for all investors. Thorough research, understanding of market dynamics, and a well-defined risk management plan are crucial before engaging in options trading. Consider consulting with a financial advisor before implementing any options strategy.
The Risks of Leverage in Options Trading
Options trading offers leverage, allowing you to control a larger position with a smaller investment. However, this leverage magnifies both profits and losses.
A small movement in the underlying asset’s price can result in a significant gain or loss on your options position. This amplified risk can quickly lead to substantial financial setbacks if the market moves against your prediction.
Time decay, or theta, is another significant risk. Options lose value as their expiration date approaches, regardless of the underlying asset’s price movement. This can be particularly detrimental if your option position isn’t profitable by the time it expires.
The complexity of options contracts also increases the risk. Understanding the various options strategies and their associated risks requires significant knowledge and experience. Improperly implemented strategies can lead to significant losses.
Therefore, while leverage can enhance potential returns, it’s crucial to carefully assess your risk tolerance and thoroughly understand the complexities of options trading before engaging in leveraged strategies. Consider starting with smaller positions and gradually increasing your exposure as you gain experience and confidence.
How to Analyze Market Trends for Options Trading
Successful options trading hinges on accurately predicting market direction. Trend analysis is crucial. Begin by identifying the overall market sentiment: is it bullish (rising), bearish (falling), or sideways (consolidating)?
Utilize technical indicators like moving averages (e.g., 50-day, 200-day) to confirm trends. A rising 50-day MA above a 200-day MA suggests an uptrend, while the opposite indicates a downtrend. Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders or triangles, can also predict potential price reversals.
Consider fundamental analysis alongside technical indicators. Examine economic data (e.g., inflation, GDP growth), company earnings reports, and geopolitical events that could significantly impact asset prices. Understanding the underlying asset’s drivers is vital.
Volume analysis provides additional insight. High volume during a price increase confirms the strength of the uptrend, while high volume during a price decrease suggests a strong downtrend. Low volume may indicate a weak trend or potential consolidation.
Remember that no analysis is foolproof. Risk management is paramount. Employ stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and diversify your options portfolio across different underlying assets and strategies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Options Trading

Options trading, while offering significant potential returns, is fraught with risks if not approached strategically. One common mistake is underestimating the time decay (theta) of options, particularly with shorter-term contracts. This can lead to substantial losses if the underlying asset doesn’t move in the desired direction before expiration.
Another frequent error is improper position sizing. Options leverage magnifies both profits and losses; therefore, entering trades with overly large positions can quickly deplete your trading capital. Always determine a risk tolerance and stick to it.
Ignoring implied volatility (IV) is another critical mistake. IV reflects the market’s expectation of price fluctuations. High IV can inflate option premiums, potentially making profitable trades difficult. Conversely, low IV might present opportunities but also limit potential gains.
Many new traders fall prey to overtrading. Attempting to make too many trades simultaneously reduces the effectiveness of risk management and can lead to emotional decision-making. Discipline and patience are crucial for long-term success in options trading.
Finally, lack of proper education and understanding is a significant pitfall. Options strategies are complex, and insufficient knowledge can result in costly mistakes. Before engaging in options trading, thorough research and perhaps professional guidance are essential.

